
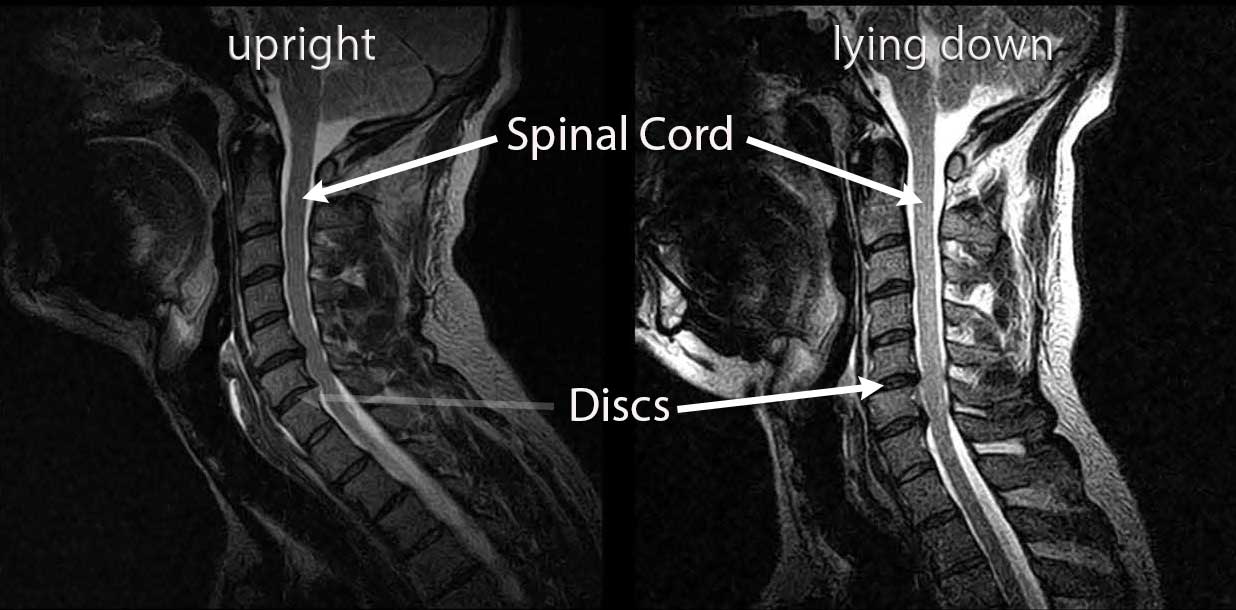
You may have trouble walking or you may fall down. Imbalance and other coordination problems.You may have trouble grasping and holding on to items. Weakness in the muscles of the arms, shoulders, or hands.Tingling or numbness in the arms, fingers, or hands.Patients with CSM may experience a combination of the following symptoms: In some patients, however, the condition may worsen more rapidly. Typically, the symptoms of CSM develop slowly and progress steadily over several years. Because these types of injuries often affect the muscles and ligaments that support the vertebrae, they may lead to spinal cord compression. For example, a "rear end" car collision may result in hyperextension, a backward motion of the neck beyond its normal limits, or hyperflexion, a forward motion of the neck beyond its normal limits. An injury to the neck-such as from a car accident, sports, or a fall-may also lead to myelopathy. When this occurs, the upper vertebra may slide forward on top of the lower vertebra, reducing the amount of space available for the spinal cord. In rheumatoid arthritis, immune cells attack the synovium, the thin membrane that lines the joints.Īs the synovium swells, it may lead to pain and stiffness and, in severe cases, destruction of the facet joints in the cervical spine. This means that the immune system attacks its own tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. Although these conditions are not related to disk degeneration, they may result in the same symptoms as CSM. Myelopathy can arise from other conditions that cause spinal cord compression, as well. A herniated disk often occurs with lifting, pulling, bending, or twisting movements. When a herniated disk bulges out toward the spinal canal, it can put pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots.Īs disks deteriorate with age, they become more prone to herniation. If the disk is very worn or injured, the nucleus may squeeze all the way through. A disk herniates when its jelly-like center (nucleus pulposus) pushes against its outer ring (annulus fibrosus). They may also make the spinal canal narrow-compressing or squeezing the spinal cord. These bone spurs contribute to the stiffening of the spine. The body responds to the collapsed disk by forming more bone-called bone spurs-around the disk to strengthen it. This problem causes settling, or collapse, of the disk spaces and loss of disk space height.Īs the disks lose height, the vertebrae move closer together. They also lose water content, begin to dry out, and become stiffer. As the disks in the spine age, they lose height and begin to bulge. These changes in the discs are often called arthritis or spondylosis. This is the soft, jelly-like center of the disk.Ĭervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is caused by changes that occur in the spine as we age. This is the tough, flexible outer ring of the disk.


Intervertebral disks are flat and round and about a half inch thick. They act as shock absorbers when you walk or run. In between your vertebrae are flexible intervertebral disks. Nerves branch out from the spinal cord through openings in the vertebrae (foramen) and carry messages between the brain and muscles. The spinal cord extends from the skull to your lower back and travels through the middle part of each stacked vertebra, called the central canal. The seven small vertebrae that begin at the base of the skull and form the neck comprise the cervical spine. Your spine is made up of 24 bones, called vertebrae that are stacked on top of one another. We offer diagnosis and treatment in over 70 specialties and subspecialties, as well as programs, services, and support to help you stay well throughout your lifetime.
#Spinal cord compression professional#
BMC physicians are leaders in their fields with the most advanced medical technology at their fingertips and working alongside a highly skilled nursing and professional staff.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
